콜백: 에이전트 행동 관찰, 사용자 정의 및 제어¶
콜백(Callbacks)은 ADK의 핵심 기능으로, 에이전트의 실행 프로세스에 연결하여 개입할 수 있는 강력한 메커니즘을 제공합니다. 콜백을 사용하면 핵심 ADK 프레임워크 코드를 수정하지 않고도 미리 정의된 특정 지점에서 에이전트의 행동을 관찰하고, 사용자 정의하며, 심지어 제어할 수 있습니다.
콜백이란 무엇인가요? 본질적으로 콜백은 여러분이 정의하는 표준 함수입니다. 그리고 에이전트를 생성할 때 이 함수들을 에이전트와 연결합니다. ADK 프레임워크는 주요 단계에서 여러분의 함수를 자동으로 호출하여 관찰하거나 개입할 수 있도록 합니다. 에이전트 프로세스 중의 체크포인트처럼 생각할 수 있습니다.
- 에이전트가 요청에 대한 주요 작업을 시작하기 전과 완료한 후: 에이전트에게 어떤 작업(예: 질문에 답변하기)을 요청하면, 에이전트는 응답을 파악하기 위해 내부 로직을 실행합니다.
Before Agent콜백은 특정 요청에 대한 이 주요 작업이 시작되기 직전에 실행됩니다.After Agent콜백은 에이전트가 해당 요청에 대한 모든 단계를 마치고 최종 결과를 준비한 직후, 하지만 결과가 반환되기 바로 전에 실행됩니다.- 이 "주요 작업"은 단일 요청을 처리하기 위한 에이전트의 전체 프로세스를 포함합니다. 이는 LLM 호출 결정, 실제 LLM 호출, 도구 사용 결정, 도구 사용, 결과 처리, 그리고 최종적으로 답변을 종합하는 과정을 포함할 수 있습니다. 이 콜백들은 본질적으로 입력을 받아 해당 상호작용에 대한 최종 출력을 생성하기까지의 전체 시퀀스를 감싸는 역할을 합니다.
- 거대 언어 모델(LLM)에 요청을 보내기 전 또는 응답을 받은 후:
Before Model,After Model콜백은 LLM으로 가고 오는 데이터를 구체적으로 검사하거나 수정할 수 있게 해줍니다. - 도구(Python 함수나 다른 에이전트 등)를 실행하기 전 또는 완료한 후: 마찬가지로,
Before Tool,After Tool콜백은 에이전트가 호출한 도구의 실행을 중심으로 제어 지점을 제공합니다.
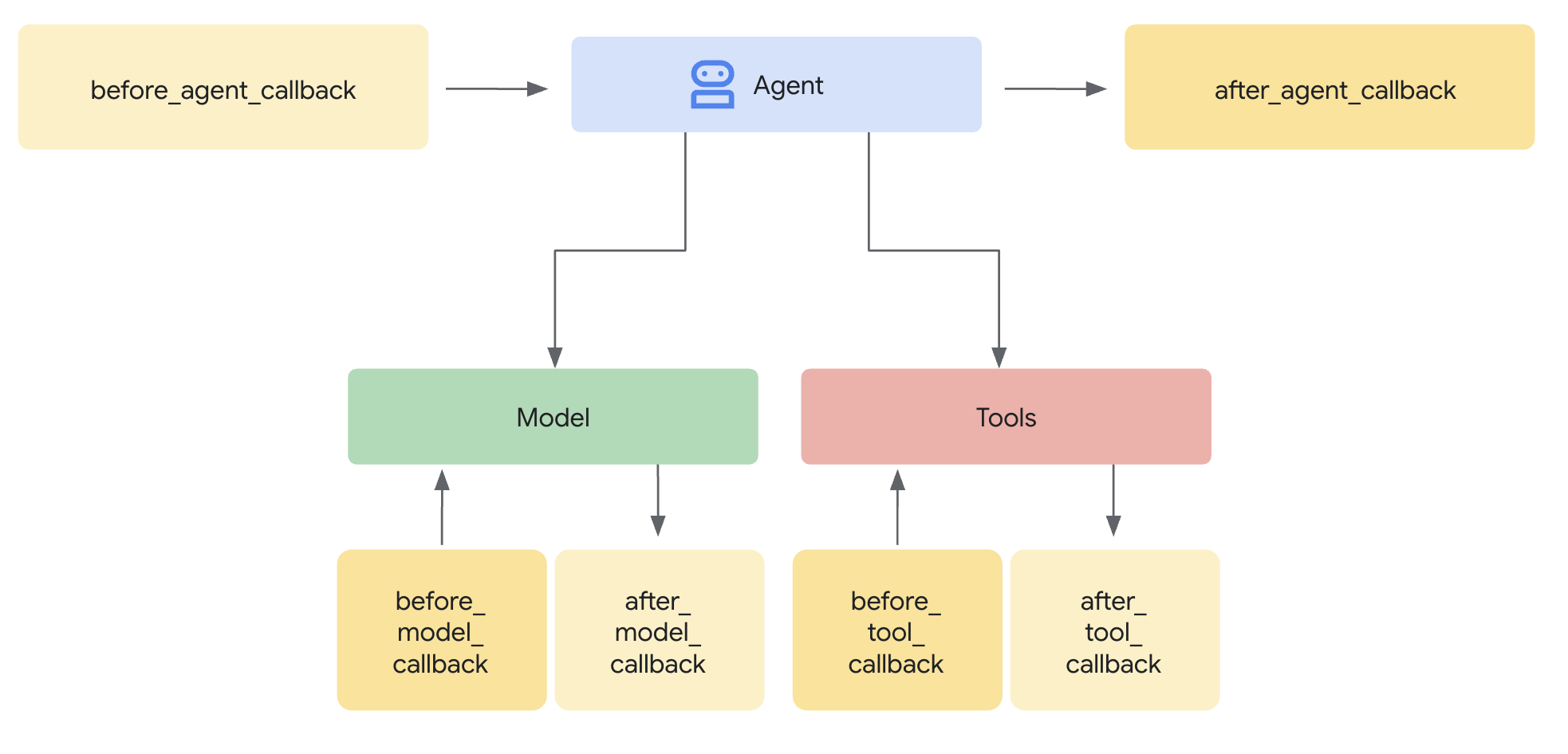
왜 사용해야 하나요? 콜백은 상당한 유연성을 제공하며 고급 에이전트 기능을 가능하게 합니다.
- 관찰 및 디버깅: 모니터링 및 문제 해결을 위해 중요한 단계에서 상세 정보를 기록합니다.
- 사용자 정의 및 제어: 에이전트를 통과하는 데이터(LLM 요청이나 도구 결과 등)를 수정하거나, 자체 로직에 따라 특정 단계를 완전히 건너뛸 수 있습니다.
- 가드레일 구현: 안전 규칙을 강제하고, 입/출력을 검증하거나, 허용되지 않는 작업을 방지합니다.
- 상태 관리: 실행 중에 에이전트의 세션 상태를 읽거나 동적으로 업데이트합니다.
- 통합 및 향상: 외부 작업(API 호출, 알림)을 트리거하거나 캐싱과 같은 기능을 추가합니다.
Tip
보안 가드레일과 정책을 구현할 때는 콜백보다 모듈성과 유연성이 더 좋은 ADK 플러그인을 사용하세요. 자세한 내용은 보안 가드레일을 위한 콜백 및 플러그인을 참조하세요.
어떻게 추가하나요:
Code
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from typing import Optional
# --- Define your callback function ---
def my_before_model_logic(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
print(f"Callback running before model call for agent: {callback_context.agent_name}")
# ... your custom logic here ...
return None # Allow the model call to proceed
# --- Register it during Agent creation ---
my_agent = LlmAgent(
name="MyCallbackAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Or your desired model
instruction="Be helpful.",
# Other agent parameters...
before_model_callback=my_before_model_logic # Pass the function here
)
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModel is a callback function that gets triggered before an LLM call.
func onBeforeModel(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModel Callback Triggered ---")
log.Printf("Model Request to be sent: %v\n", req)
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runBasicExample() {
const (
appName = "CallbackBasicApp"
userID = "test_user_123"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
// Register the callback function in the agent configuration.
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "SimpleAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModel},
}
simpleAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: simpleAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.Callbacks;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import java.util.Optional;
public class AgentWithBeforeModelCallback {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- Define your callback logic ---
Callbacks.BeforeModelCallbackSync myBeforeModelLogic =
(CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) -> {
System.out.println(
"Callback running before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// ... your custom logic here ...
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the model call to proceed,
// similar to returning None in the Python example.
// If you wanted to return a response and skip the model call,
// you would return Optional.of(yourLlmResponse).
return Optional.empty();
};
// --- Register it during Agent creation ---
LlmAgent myAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("MyCallbackAgent")
.model("gemini-2.0-flash") // Or your desired model
.instruction("Be helpful.")
// Other agent parameters...
.beforeModelCallbackSync(myBeforeModelLogic) // Pass the callback implementation here
.build();
}
}
콜백 메커니즘: 가로채기와 제어¶
ADK 프레임워크가 콜백이 실행될 수 있는 지점(예: LLM을 호출하기 직전)에 도달하면, 해당 에이전트에 대해 상응하는 콜백 함수를 제공했는지 확인합니다. 만약 제공했다면 프레임워크는 여러분의 함수를 실행합니다.
컨텍스트가 중요합니다: 콜백 함수는 독립적으로 호출되지 않습니다. 프레임워크는 특별한 컨텍스트 객체(CallbackContext 또는 ToolContext)를 인수로 제공합니다. 이 객체들은 호출 세부 정보, 세션 상태, 그리고 아티팩트나 메모리와 같은 서비스에 대한 참조를 포함하여 에이전트 실행의 현재 상태에 대한 중요한 정보를 담고 있습니다. 여러분은 이 컨텍스트 객체를 사용하여 상황을 이해하고 프레임워크와 상호작용합니다. (자세한 내용은 "컨텍스트 객체" 전용 섹션을 참조하세요).
흐름 제어 (핵심 메커니즘): 콜백의 가장 강력한 측면은 반환 값이 에이전트의 후속 작업에 어떻게 영향을 미치는지에 있습니다. 이를 통해 실행 흐름을 가로채고 제어할 수 있습니다.
-
return None(기본 동작 허용):- 특정 반환 타입은 언어에 따라 다를 수 있습니다. Java에서는
Optional.empty()가 이에 해당합니다. 언어별 지침은 API 문서를 참조하세요. - 이는 콜백이 자신의 작업(예: 로깅, 검사,
llm_request와 같은 변경 가능한 입력 인수의 약간의 수정)을 마쳤으며 ADK 에이전트가 정상적인 작업을 계속 진행해야 함을 알리는 표준 방식입니다. before_*콜백(before_agent,before_model,before_tool)의 경우None을 반환하면 다음 단계(에이전트 로직 실행, LLM 호출, 도구 실행)가 발생합니다.after_*콜백(after_agent,after_model,after_tool)의 경우None을 반환하면 바로 이전 단계에서 생성된 결과(에이전트의 출력, LLM의 응답, 도구의 결과)가 그대로 사용됩니다.
- 특정 반환 타입은 언어에 따라 다를 수 있습니다. Java에서는
-
return <특정 객체>(기본 동작 재정의):None대신 특정 타입의 객체를 반환하는 것은 ADK 에이전트의 기본 동작을 재정의(override)하는 방법입니다. 프레임워크는 여러분이 반환한 객체를 사용하고, 정상적으로 뒤따랐을 단계를 건너뛰거나 방금 생성된 결과를 대체합니다.before_agent_callback→types.Content: 에이전트의 주 실행 로직(_run_async_impl/_run_live_impl)을 건너뜁니다. 반환된Content객체는 즉시 해당 턴에 대한 에이전트의 최종 출력으로 처리됩니다. 간단한 요청을 직접 처리하거나 접근 제어를 강제하는 데 유용합니다.before_model_callback→LlmResponse: 외부 거대 언어 모델 호출을 건너뜁니다. 반환된LlmResponse객체는 마치 LLM의 실제 응답인 것처럼 처리됩니다. 입력 가드레일 구현, 프롬프트 검증, 또는 캐시된 응답을 제공하는 데 이상적입니다.before_tool_callback→dict또는Map: 실제 도구 함수(또는 하위 에이전트)의 실행을 건너뜁니다. 반환된dict는 도구 호출의 결과로 사용되며, 이는 일반적으로 LLM에 다시 전달됩니다. 도구 인자 검증, 정책 제한 적용, 또는 모의/캐시된 도구 결과를 반환하는 데 완벽합니다.after_agent_callback→types.Content: 에이전트의 실행 로직이 방금 생성한Content를 대체합니다.after_model_callback→LlmResponse: LLM으로부터 받은LlmResponse를 대체합니다. 출력 내용을 정제하거나, 표준 면책 조항을 추가하거나, LLM의 응답 구조를 수정하는 데 유용합니다.after_tool_callback→dict또는Map: 도구가 반환한dict결과를 대체합니다. 도구 출력을 LLM에 다시 보내기 전에 후처리하거나 표준화할 수 있습니다.
개념적 코드 예제 (가드레일):
이 예제는 before_model_callback을 사용한 가드레일의 일반적인 패턴을 보여줍니다.
Code
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from typing import Optional
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
GEMINI_2_FLASH="gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Define the Callback Function ---
def simple_before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
"""Inspects/modifies the LLM request or skips the call."""
agent_name = callback_context.agent_name
print(f"[Callback] Before model call for agent: {agent_name}")
# Inspect the last user message in the request contents
last_user_message = ""
if llm_request.contents and llm_request.contents[-1].role == 'user':
if llm_request.contents[-1].parts:
last_user_message = llm_request.contents[-1].parts[0].text
print(f"[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '{last_user_message}'")
# --- Modification Example ---
# Add a prefix to the system instruction
original_instruction = llm_request.config.system_instruction or types.Content(role="system", parts=[])
prefix = "[Modified by Callback] "
# Ensure system_instruction is Content and parts list exists
if not isinstance(original_instruction, types.Content):
# Handle case where it might be a string (though config expects Content)
original_instruction = types.Content(role="system", parts=[types.Part(text=str(original_instruction))])
if not original_instruction.parts:
original_instruction.parts.append(types.Part(text="")) # Add an empty part if none exist
# Modify the text of the first part
modified_text = prefix + (original_instruction.parts[0].text or "")
original_instruction.parts[0].text = modified_text
llm_request.config.system_instruction = original_instruction
print(f"[Callback] Modified system instruction to: '{modified_text}'")
# --- Skip Example ---
# Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if "BLOCK" in last_user_message.upper():
print("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.")
# Return an LlmResponse to skip the actual LLM call
return LlmResponse(
content=types.Content(
role="model",
parts=[types.Part(text="LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")],
)
)
else:
print("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.")
# Return None to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return None
# Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback
my_llm_agent = LlmAgent(
name="ModelCallbackAgent",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="You are a helpful assistant.", # Base instruction
description="An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback",
before_model_callback=simple_before_model_modifier # Assign the function here
)
APP_NAME = "guardrail_app"
USER_ID = "user_1"
SESSION_ID = "session_001"
# Session and Runner
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=my_llm_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
return session, runner
# Agent Interaction
async def call_agent_async(query):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
session, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("write a joke on BLOCK")
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModelGuardrail is a callback that inspects the LLM request.
// If it contains a forbidden topic, it blocks the request and returns a
// predefined response. Otherwise, it allows the request to proceed.
func onBeforeModelGuardrail(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModelGuardrail Callback Triggered ---")
// Inspect the request content for forbidden topics.
for _, content := range req.Contents {
for _, part := range content.Parts {
if strings.Contains(part.Text, "finance") {
log.Println("Forbidden topic 'finance' detected. Blocking LLM call.")
// By returning a non-nil response, we override the default behavior
// and prevent the actual LLM call.
return &model.LLMResponse{
Content: &genai.Content{
Parts: []*genai.Part{{Text: "I'm sorry, but I cannot discuss financial topics."}},
Role: "model",
},
}, nil
}
}
}
log.Println("No forbidden topics found. Allowing LLM call to proceed.")
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runGuardrailExample() {
const (
appName = "GuardrailApp"
userID = "test_user_456"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "ChatAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModelGuardrail},
}
chatAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: chatAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.events.Event;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmResponse;
import com.google.adk.runner.InMemoryRunner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.GenerateContentConfig;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class BeforeModelGuardrailExample {
private static final String MODEL_ID = "gemini-2.0-flash";
private static final String APP_NAME = "guardrail_app";
private static final String USER_ID = "user_1";
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeforeModelGuardrailExample example = new BeforeModelGuardrailExample();
example.defineAgentAndRun("Tell me about quantum computing. This is a test.");
}
// --- Define your callback logic ---
// Looks for the word "BLOCK" in the user prompt and blocks the call to LLM if found.
// Otherwise the LLM call proceeds as usual.
public Optional<LlmResponse> simpleBeforeModelModifier(
CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) {
System.out.println("[Callback] Before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// Inspect the last user message in the request contents
String lastUserMessageText = "";
List<Content> requestContents = llmRequest.contents();
if (requestContents != null && !requestContents.isEmpty()) {
Content lastContent = requestContents.get(requestContents.size() - 1);
if (lastContent.role().isPresent() && "user".equals(lastContent.role().get())) {
lastUserMessageText =
lastContent.parts().orElse(List.of()).stream()
.flatMap(part -> part.text().stream())
.collect(Collectors.joining(" ")); // Concatenate text from all parts
}
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '" + lastUserMessageText + "'");
String prefix = "[Modified by Callback] ";
GenerateContentConfig currentConfig =
llmRequest.config().orElse(GenerateContentConfig.builder().build());
Optional<Content> optOriginalSystemInstruction = currentConfig.systemInstruction();
Content conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction;
if (optOriginalSystemInstruction.isPresent()) {
Content originalSystemInstruction = optOriginalSystemInstruction.get();
List<Part> originalParts =
new ArrayList<>(originalSystemInstruction.parts().orElse(List.of()));
String originalText = "";
if (!originalParts.isEmpty()) {
Part firstPart = originalParts.get(0);
if (firstPart.text().isPresent()) {
originalText = firstPart.text().get();
}
originalParts.set(0, Part.fromText(prefix + originalText));
} else {
originalParts.add(Part.fromText(prefix));
}
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
originalSystemInstruction.toBuilder().parts(originalParts).build();
} else {
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
Content.builder()
.role("system")
.parts(List.of(Part.fromText(prefix)))
.build();
}
// This demonstrates building a new LlmRequest with the modified config.
llmRequest =
llmRequest.toBuilder()
.config(
currentConfig.toBuilder()
.systemInstruction(conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction)
.build())
.build();
System.out.println(
"[Callback] Conceptually modified system instruction is: '"
+ llmRequest.config().get().systemInstruction().get().parts().get().get(0).text().get());
// --- Skip Example ---
// Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if (lastUserMessageText.toUpperCase().contains("BLOCK")) {
System.out.println("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.");
LlmResponse skipResponse =
LlmResponse.builder()
.content(
Content.builder()
.role("model")
.parts(
List.of(
Part.builder()
.text("LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")
.build()))
.build())
.build();
return Optional.of(skipResponse);
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.");
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return Optional.empty();
}
public void defineAgentAndRun(String prompt) {
// --- Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback ---
LlmAgent myLlmAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ModelCallbackAgent")
.model(MODEL_ID)
.instruction("You are a helpful assistant.") // Base instruction
.description("An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback")
.beforeModelCallbackSync(this::simpleBeforeModelModifier) // Assign the callback here
.build();
// Session and Runner
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(myLlmAgent, APP_NAME);
// InMemoryRunner automatically creates a session service. Create a session using the service
Session session = runner.sessionService().createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID).blockingGet();
Content userMessage =
Content.fromParts(Part.fromText(prompt));
// Run the agent
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
// Stream event response
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse()) {
System.out.println(event.stringifyContent());
}
});
}
}
None을 반환하는 것과 특정 객체를 반환하는 것의 차이를 이해함으로써 에이전트의 실행 경로를 정밀하게 제어할 수 있으며, 이는 ADK로 정교하고 신뢰할 수 있는 에이전트를 구축하는 데 있어 콜백을 필수적인 도구로 만들어 줍니다.