カスタムエージェント¶
カスタムエージェントは、BaseAgentを直接継承し、独自の制御フローを実装することで任意のオーケストレーションロジックを定義でき、ADKにおいて究極の柔軟性を提供します。これは、SequentialAgent、LoopAgent、ParallelAgentといった事前定義されたパターンを超え、非常に特殊で複雑なエージェントワークフローを構築することを可能にします。
高度な概念
_run_async_impl(または他の言語での同等のメソッド)を直接実装してカスタムエージェントを構築することは、強力な制御を提供しますが、事前定義されたLlmAgentや標準のWorkflowAgentタイプを使用するよりも複雑です。カスタムオーケストレーションロジックに取り組む前に、これらの基本的なエージェントタイプをまず理解することをお勧めします。
はじめに:事前定義されたワークフローを超えて¶
カスタムエージェントとは?¶
カスタムエージェントとは、本質的にgoogle.adk.agents.BaseAgentを継承し、その中核となる実行ロジックを_run_async_impl非同期メソッド内に実装して作成する任意のクラスです。このメソッドが他のエージェント(サブエージェント)をどのように呼び出し、状態を管理し、イベントを処理するかを完全に制御できます。
Note
エージェントの中核となる非同期ロジックを実装するための特定のメソッド名は、SDKの言語によって若干異なる場合があります(例:JavaではrunAsyncImpl、Pythonでは_run_async_impl)。詳細は、各言語のAPIドキュメントを参照してください。
なぜ使用するのか?¶
標準のワークフローエージェント(SequentialAgent、LoopAgent、ParallelAgent)は一般的なオーケストレーションパターンをカバーしていますが、要件に以下が含まれる場合はカスタムエージェントが必要になります。
- 条件付きロジック: 実行時の条件や前のステップの結果に基づいて、異なるサブエージェントを実行したり、異なるパスをたどる場合。
- 複雑な状態管理: 単純な逐次的な受け渡しを超えて、ワークフロー全体で状態を維持・更新するための複雑なロジックを実装する場合。
- 外部との統合: オーケストレーションのフロー制御内で、外部API、データベース、またはカスタムライブラリへの呼び出しを直接組み込む場合。
- 動的なエージェント選択: 状況や入力の動的な評価に基づいて、次に実行するサブエージェントを選択する場合。
- 独自のワークフローパターン: 標準的なシーケンシャル、パラレル、またはループ構造に適合しないオーケストレーションロジックを実装する場合。
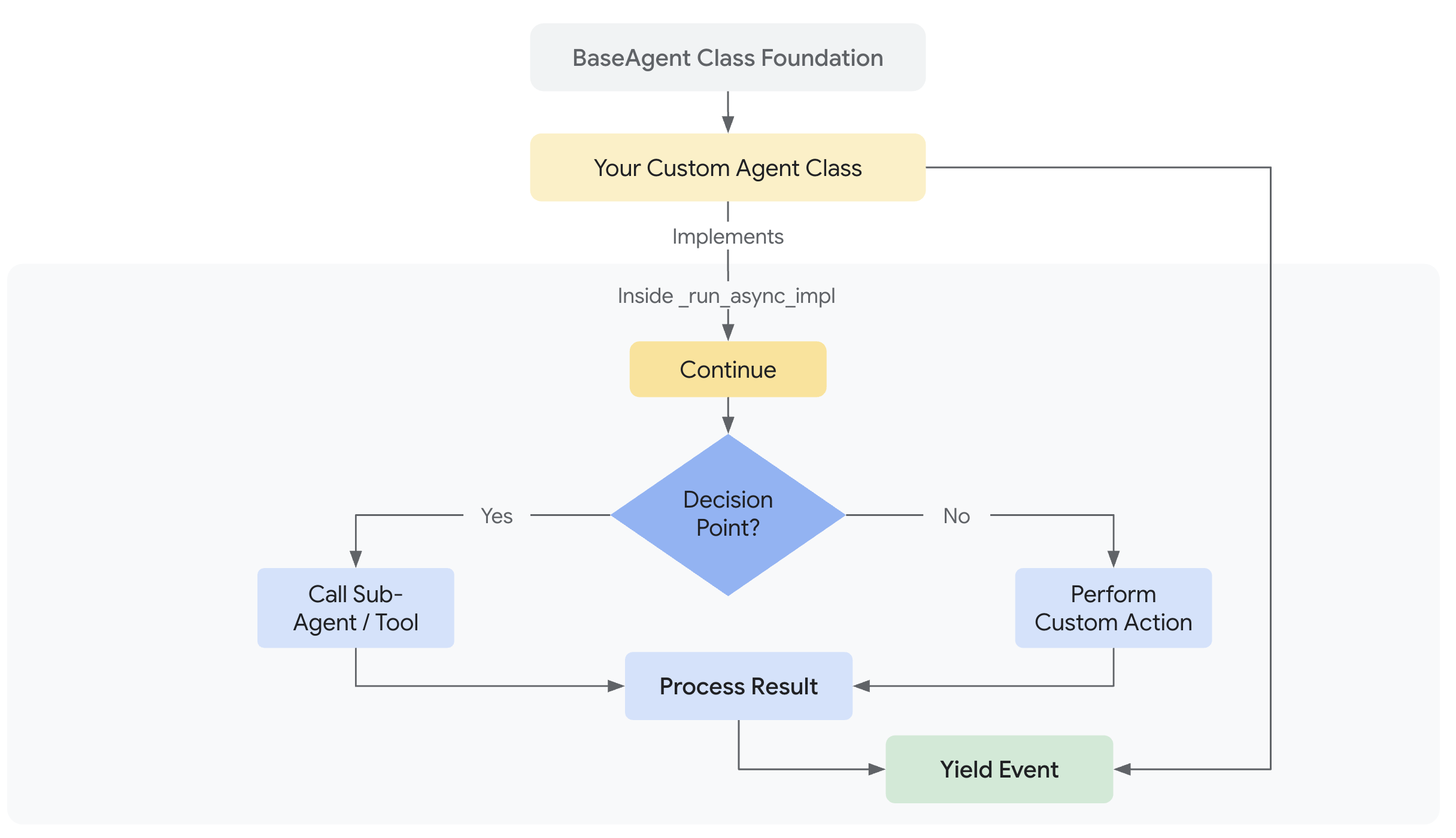
カスタムロジックの実装:¶
すべてのカスタムエージェントの中核は、その独自の非同期動作を定義するメソッドです。このメソッドにより、サブエージェントをオーケストレーションし、実行の流れを管理できます。
すべてのカスタムエージェントの中心は_run_async_implメソッドです。ここで独自の動作を定義します。
- シグネチャ:
async def _run_async_impl(self, ctx: InvocationContext) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]: - 非同期ジェネレーター:
async def関数であり、AsyncGeneratorを返す必要があります。これにより、サブエージェントや自身のロジックによって生成されたイベントをyieldでランナーに返すことができます。 ctx(InvocationContext): 重要な実行時情報、特にctx.session.stateへのアクセスを提供します。これは、カスタムエージェントがオーケストレーションするステップ間でデータを共有する主要な方法です。
Goでは、agent.Agentインターフェースを満たす構造体の一部としてRunメソッドを実装します。実際のロジックは通常、カスタムエージェント構造体のメソッドとなります。
- シグネチャ:
Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] - イテレータ:
Runメソッドは、イベントとエラーを生成するイテレータ(iter.Seq2)を返します。これは、エージェントの実行からストリーミング結果を処理する標準的な方法です。 ctx(InvocationContext):agent.InvocationContextは、状態を含むセッションやその他の重要な実行時情報へのアクセスを提供します。- セッション状態:
ctx.Session().State()を介してセッション状態にアクセスできます。
すべてのカスタムエージェントの中心は、BaseAgentからオーバーライドするrunAsyncImplメソッドです。
- シグネチャ:
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext ctx) - リアクティブストリーム (
Flowable):io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable<Event>を返す必要があります。このFlowableは、カスタムエージェントのロジックによって生成されるイベントのストリームを表し、しばしば複数のサブエージェントからのFlowableを組み合わせたり変換したりして作成されます。 ctx(InvocationContext): 重要な実行時情報、特にjava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap<String, Object>であるctx.session().state()へのアクセスを提供します。これは、カスタムエージェントがオーケストレーションするステップ間でデータを共有する主要な方法です。
中核となる非同期メソッド内の主要な機能:
-
サブエージェントの呼び出し:
run_asyncメソッドを使用して(通常はself.my_llm_agentなどのインスタンス属性として格納されている)サブエージェントを呼び出し、そのイベントをyieldします。 -
状態管理: セッション状態辞書(
ctx.session.state)の読み書きを行い、サブエージェントの呼び出し間でデータを渡したり、意思決定を行ったりします。 -
制御フローの実装: 標準のPython構文(
if/elif/else、for/whileループ、try/except)を使用して、サブエージェントを含む洗練された、条件付きまたは反復的なワークフローを作成します。
-
サブエージェントの呼び出し:
Runメソッドを呼び出してサブエージェントを起動します。 -
状態管理: セッション状態の読み書きを行い、サブエージェントの呼び出し間でデータを渡したり、意思決定を行ったりします。
// `ctx`(`agent.InvocationContext`)はエージェントの`Run`関数に直接渡される // 前のエージェントが設定したデータを読み込む previousResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("some_key") if err != nil { // キーがまだ存在しない可能性のあるケースを処理 } // 状態に基づいて意思決定 if val, ok := previousResult.(string); ok && val == "some_value" { // ... 特定のサブエージェントを呼び出す ... } else { // ... 別のサブエージェントを呼び出す ... } // 後のステップのために結果を保存する if err := ctx.Session().State().Set("my_custom_result", "calculated_value"); err != nil { // エラー処理 } -
制御フローの実装: 標準のGo構文(
if/else、for/switchループ、ゴルーチン、チャネル)を使用して、サブエージェントを含む洗練された、条件付きまたは反復的なワークフローを作成します。
-
サブエージェントの呼び出し: 非同期実行メソッドを使用して(通常はインスタンス属性やオブジェクトとして格納されている)サブエージェントを呼び出し、そのイベントストリームを返します。
通常、
concatWith、flatMapPublisher、concatArrayなどのRxJava演算子を使用して、サブエージェントからのFlowableを連鎖させます。// 例:サブエージェントを1つ実行 // return someSubAgent.runAsync(ctx); // 例:サブエージェントを順次実行 Flowable<Event> firstAgentEvents = someSubAgent1.runAsync(ctx) .doOnNext(event -> System.out.println("エージェント1からのイベント: " + event.id())); Flowable<Event> secondAgentEvents = Flowable.defer(() -> someSubAgent2.runAsync(ctx) .doOnNext(event -> System.out.println("エージェント2からのイベント: " + event.id())) ); return firstAgentEvents.concatWith(secondAgentEvents);Flowable.defer()は、後続ステージの実行が前のステージの完了や状態に依存する場合によく使用されます。 -
状態管理: セッション状態の読み書きを行い、サブエージェントの呼び出し間でデータを渡したり、意思決定を行ったりします。セッション状態は
ctx.session().state()を介して取得されるjava.util.concurrent.ConcurrentMap<String, Object>です。// 前のエージェントが設定したデータを読み込む Object previousResult = ctx.session().state().get("some_key"); // 状態に基づいて意思決定 if ("some_value".equals(previousResult)) { // ... 特定のサブエージェントのFlowableを含めるロジック ... } else { // ... 別のサブエージェントのFlowableを含めるロジック ... } // 後のステップのために結果を保存する(サブエージェントのoutput_keyを介して行われることが多い) // ctx.session().state().put("my_custom_result", "calculated_value"); -
制御フローの実装: 標準の言語構文(
if/else、ループ、try/catch)とリアクティブ演算子(RxJava)を組み合わせて、洗練されたワークフローを作成します。- 条件付き: 条件に基づいてどの
Flowableを購読するかを選択するためのFlowable.defer()、またはストリーム内でイベントをフィルタリングする場合はfilter()。 - 反復:
repeat()、retry()などの演算子、または条件に基づいてFlowableチェーンの一部を再帰的に呼び出すように構造化する(flatMapPublisherやconcatMapで管理されることが多い)。
- 条件付き: 条件に基づいてどの
サブエージェントと状態の管理¶
通常、カスタムエージェントは他のエージェント(LlmAgent、LoopAgentなど)をオーケストレーションします。
- 初期化: 通常、これらのサブエージェントのインスタンスをカスタムエージェントのコンストラクタに渡し、インスタンスフィールド/属性として格納します(例:
this.story_generator = story_generator_instanceまたはself.story_generator = story_generator_instance)。これにより、カスタムエージェントの中核となる非同期実行ロジック(_run_async_implメソッドなど)内からアクセス可能になります。 - サブエージェントリスト:
super()コンストラクタを使用してBaseAgentを初期化する際に、sub agentsリストを渡すべきです。このリストは、このカスタムエージェントの直接の階層に属するエージェントをADKフレームワークに伝えます。これは、中核となる実行ロジック(_run_async_impl)がself.xxx_agentを介してエージェントを直接呼び出す場合でも、ライフサイクル管理、イントロスペクション、そして将来のルーティング機能などのフレームワーク機能にとって重要です。カスタムロジックがトップレベルで直接呼び出すエージェントを含めてください。 - 状態: 前述の通り、
ctx.session.stateは、サブエージェント(特にoutput keyを使用するLlmAgent)が結果をオーケストレーターに返し、オーケストレーターが必要な入力を渡すための標準的な方法です。
デザインパターン例: StoryFlowAgent¶
条件付きロジックを持つ多段階のコンテンツ生成ワークフローという例のパターンで、カスタムエージェントの強力さを示しましょう。
目標: 物語を生成し、批評と修正を通じて反復的に洗練させ、最終チェックを行い、そして重要なことに、最終的なトーンチェックに失敗した場合は物語を再生成するシステムを作成します。
なぜカスタムか? ここでカスタムエージェントが必要となる中核的な要件は、トーンチェックに基づく条件付き再生成です。標準のワークフローエージェントには、サブエージェントのタスクの結果に基づく条件分岐機能が組み込まれていません。オーケストレーター内にカスタムロジック(if tone == "negative": ...)が必要です。
パート1:簡略化されたカスタムエージェントの初期化¶
BaseAgentを継承するStoryFlowAgentを定義します。__init__では、(渡された)必要なサブエージェントをインスタンス属性として格納し、このカスタムエージェントが直接オーケストレーションするトップレベルのエージェントをBaseAgentフレームワークに伝えます。
class StoryFlowAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
Custom agent for a story generation and refinement workflow.
This agent orchestrates a sequence of LLM agents to generate a story,
critique it, revise it, check grammar and tone, and potentially
regenerate the story if the tone is negative.
"""
# --- Field Declarations for Pydantic ---
# Declare the agents passed during initialization as class attributes with type hints
story_generator: LlmAgent
critic: LlmAgent
reviser: LlmAgent
grammar_check: LlmAgent
tone_check: LlmAgent
loop_agent: LoopAgent
sequential_agent: SequentialAgent
# model_config allows setting Pydantic configurations if needed, e.g., arbitrary_types_allowed
model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}
def __init__(
self,
name: str,
story_generator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammar_check: LlmAgent,
tone_check: LlmAgent,
):
"""
Initializes the StoryFlowAgent.
Args:
name: The name of the agent.
story_generator: An LlmAgent to generate the initial story.
critic: An LlmAgent to critique the story.
reviser: An LlmAgent to revise the story based on criticism.
grammar_check: An LlmAgent to check the grammar.
tone_check: An LlmAgent to analyze the tone.
"""
# Create internal agents *before* calling super().__init__
loop_agent = LoopAgent(
name="CriticReviserLoop", sub_agents=[critic, reviser], max_iterations=2
)
sequential_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="PostProcessing", sub_agents=[grammar_check, tone_check]
)
# Define the sub_agents list for the framework
sub_agents_list = [
story_generator,
loop_agent,
sequential_agent,
]
# Pydantic will validate and assign them based on the class annotations.
super().__init__(
name=name,
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
loop_agent=loop_agent,
sequential_agent=sequential_agent,
sub_agents=sub_agents_list, # Pass the sub_agents list directly
)
StoryFlowAgent構造体とコンストラクタを定義します。コンストラクタでは、必要なサブエージェントを格納し、このカスタムエージェントが直接オーケストレーションするトップレベルのエージェントをBaseAgentフレームワークに伝えます。
// StoryFlowAgent is a custom agent that orchestrates a story generation workflow.
// It encapsulates the logic of running sub-agents in a specific sequence.
type StoryFlowAgent struct {
storyGenerator agent.Agent
revisionLoopAgent agent.Agent
postProcessorAgent agent.Agent
}
// NewStoryFlowAgent creates and configures the entire custom agent workflow.
// It takes individual LLM agents as input and internally creates the necessary
// workflow agents (loop, sequential), returning the final orchestrator agent.
func NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck agent.Agent,
) (agent.Agent, error) {
loopAgent, err := loopagent.New(loopagent.Config{
MaxIterations: 2,
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "CriticReviserLoop",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{critic, reviser},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create loop agent: %w", err)
}
sequentialAgent, err := sequentialagent.New(sequentialagent.Config{
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "PostProcessing",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{grammarCheck, toneCheck},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create sequential agent: %w", err)
}
// The StoryFlowAgent struct holds the agents needed for the Run method.
orchestrator := &StoryFlowAgent{
storyGenerator: storyGenerator,
revisionLoopAgent: loopAgent,
postProcessorAgent: sequentialAgent,
}
// agent.New creates the final agent, wiring up the Run method.
return agent.New(agent.Config{
Name: "StoryFlowAgent",
Description: "Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent},
Run: orchestrator.Run,
})
}
BaseAgentを拡張してStoryFlowAgentExampleを定義します。そのコンストラクタで、(パラメータとして渡された)必要なサブエージェントのインスタンスをインスタンスフィールドとして格納します。このカスタムエージェントが直接オーケストレーションするこれらのトップレベルのサブエージェントは、BaseAgentのsuperコンストラクタにもリストとして渡されます。
private final LlmAgent storyGenerator;
private final LoopAgent loopAgent;
private final SequentialAgent sequentialAgent;
public StoryFlowAgentExample(
String name, LlmAgent storyGenerator, LoopAgent loopAgent, SequentialAgent sequentialAgent) {
super(
name,
"Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
List.of(storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent),
null,
null);
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
パート2:カスタム実行ロジックの定義¶
このメソッドは、標準のPython async/awaitと制御フローを使用してサブエージェントをオーケストレーションします。
@override
async def _run_async_impl(
self, ctx: InvocationContext
) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]:
"""
Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
"""
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Starting story generation workflow.")
# 1. Initial Story Generation
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running StoryGenerator...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# Check if story was generated before proceeding
if "current_story" not in ctx.session.state or not ctx.session.state["current_story"]:
logger.error(f"[{self.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return # Stop processing if initial story failed
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after generator: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...")
# Use the loop_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.loop_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after loop: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running PostProcessing...")
# Use the sequential_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.sequential_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from PostProcessing: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
tone_check_result = ctx.session.state.get("tone_check_result")
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone check result: {tone_check_result}")
if tone_check_result == "negative":
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
else:
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
pass
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Workflow finished.")
- 初期の
story_generatorが実行されます。その出力はctx.session.state["current_story"]にあると期待されます。 loop_agentが実行され、内部でcriticとreviserをmax_iterations回、順次呼び出します。これらは状態からcurrent_storyとcriticismを読み書きします。sequential_agentが実行され、grammar_check、次にtone_checkを呼び出し、current_storyを読み込んでgrammar_suggestionsとtone_check_resultを状態に書き込みます。- カスタム部分:
if文が状態からtone_check_resultをチェックします。もし"negative"であれば、story_generatorが再度呼び出され、状態のcurrent_storyを上書きします。そうでなければ、フローは終了します。
Runメソッドは、各サブエージェントのRunメソッドをループ内で呼び出し、そのイベントをyieldすることでサブエージェントをオーケストレーションします。
// Run defines the custom execution logic for the StoryFlowAgent.
func (s *StoryFlowAgent) Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] {
return func(yield func(*session.Event, error) bool) {
// Stage 1: Initial Story Generation
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story generator failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Check if story was generated before proceeding
currentStory, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("current_story")
if err != nil || currentStory == "" {
log.Println("Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return
}
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop
for event, err := range s.revisionLoopAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("loop agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 3: Post-Processing
for event, err := range s.postProcessorAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("sequential agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration
toneResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("tone_check_result")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Could not read tone_check_result from state: %v. Assuming tone is not negative.", err)
return
}
if tone, ok := toneResult.(string); ok && tone == "negative" {
log.Println("Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story regeneration failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
} else {
log.Println("Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
}
}
}
- 初期の
storyGeneratorが実行されます。その出力はセッション状態のキー"current_story"にあると期待されます。 revisionLoopAgentが実行され、内部でcriticとreviserをmax_iterations回、順次呼び出します。これらは状態からcurrent_storyとcriticismを読み書きします。postProcessorAgentが実行され、grammar_check、次にtone_checkを呼び出し、current_storyを読み込んでgrammar_suggestionsとtone_check_resultを状態に書き込みます。- カスタム部分: コードが状態から
tone_check_resultをチェックします。もし"negative"であれば、story_generatorが再度呼び出され、状態のcurrent_storyを上書きします。そうでなければ、フローは終了します。
runAsyncImplメソッドは、RxJavaのFlowableストリームと演算子を使用して、非同期制御フローでサブエージェントをオーケストレーションします。
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
// Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Starting story generation workflow.", name()));
// Stage 1. Initial Story Generation
Flowable<Event> storyGenFlow = runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator");
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop (runs after story generation completes)
Flowable<Event> criticReviserFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
if (!isStoryGenerated(invocationContext)) {
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,() ->
String.format("[%s] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting after StoryGenerator.",
name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // Stop further processing if no story
}
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after generator: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(loopAgent, invocationContext, "CriticReviserLoop");
});
// Stage 3: Post-Processing (runs after critic-reviser loop completes)
Flowable<Event> postProcessingFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after loop: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(sequentialAgent, invocationContext, "PostProcessing");
});
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration (runs after post-processing completes)
Flowable<Event> conditionalRegenFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
String toneCheckResult = (String) invocationContext.session().state().get("tone_check_result");
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Tone check result: %s", name(), toneCheckResult));
if ("negative".equalsIgnoreCase(toneCheckResult)) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...", name()));
return runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator (Regen)");
} else {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.", name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // No regeneration needed
}
});
return Flowable.concatArray(storyGenFlow, criticReviserFlow, postProcessingFlow, conditionalRegenFlow)
.doOnComplete(() -> logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Workflow finished.", name())));
}
// Helper method for a single agent run stage with logging
private Flowable<Event> runStage(BaseAgent agentToRun, InvocationContext ctx, String stageName) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Running %s...", name(), stageName));
return agentToRun
.runAsync(ctx)
.doOnNext(event ->
logger.log(Level.INFO,() ->
String.format("[%s] Event from %s: %s", name(), stageName, event.toJson())))
.doOnError(err ->
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,
String.format("[%s] Error in %s", name(), stageName), err))
.doOnComplete(() ->
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] %s finished.", name(), stageName)));
}
- 初期の
storyGenerator.runAsync(invocationContext)Flowableが実行されます。その出力はinvocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")にあると期待されます。 - (
Flowable.concatArrayとFlowable.deferにより)loopAgentのFlowableが次に実行されます。LoopAgentは内部でcriticとreviserサブエージェントを最大maxIterations回、順次呼び出します。これらは状態からcurrent_storyとcriticismを読み書きします。 - 次に、
sequentialAgentのFlowableが実行されます。これはgrammar_check、次にtone_checkを呼び出し、current_storyを読み込んでgrammar_suggestionsとtone_check_resultを状態に書き込みます。 - カスタム部分: sequentialAgentが完了した後、
Flowable.defer内のロジックがinvocationContext.session().state()から"tone_check_result"をチェックします。もし"negative"であれば、storyGeneratorのFlowableが条件付きで連結されて再度実行され、"current_story"を上書きします。そうでなければ、空のFlowableが使用され、全体のワークフローは完了へと進みます。
パート3:LLMサブエージェントの定義¶
これらは特定のタスクを担当する標準のLlmAgent定義です。output keyパラメータは、結果をsession.stateに配置し、他のエージェントやカスタムオーケストレーターがアクセスできるようにするために重要です。
指示文への状態の直接注入
story_generatorの指示文に注目してください。{var}構文はプレースホルダーです。指示文がLLMに送信される前に、ADKフレームワークは自動的に(例:{topic})をsession.state['topic']の値に置き換えます。これは、指示文内でテンプレートを使用してエージェントにコンテキストを提供する推奨方法です。詳細は、状態のドキュメントを参照してください。
GEMINI_2_FLASH = "gemini-2.0-flash" # モデル定数を定義
# --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
story_generator = LlmAgent(
name="StoryGenerator",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Key for storing output in session state
)
critic = LlmAgent(
name="Critic",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="criticism", # Key for storing criticism in session state
)
reviser = LlmAgent(
name="Reviser",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Overwrites the original story
)
grammar_check = LlmAgent(
name="GrammarCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="grammar_suggestions",
)
tone_check = LlmAgent(
name="ToneCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="tone_check_result", # This agent's output determines the conditional flow
)
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
LlmAgent storyGenerator =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("StoryGenerator")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Generates the initial story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat,
based on the topic: {topic}
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Key for storing output in session state
.build();
LlmAgent critic =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Critic")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Critiques the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("criticism") // Key for storing criticism in session state
.build();
LlmAgent reviser =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Reviser")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Revises the story based on criticism.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Overwrites the original story
.build();
LlmAgent grammarCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("GrammarCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Checks grammar and suggests corrections.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.
""")
.outputKey("grammar_suggestions")
.build();
LlmAgent toneCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ToneCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Analyzes the tone of the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.
""")
.outputKey("tone_check_result") // This agent's output determines the conditional flow
.build();
LoopAgent loopAgent =
LoopAgent.builder()
.name("CriticReviserLoop")
.description("Iteratively critiques and revises the story.")
.subAgents(critic, reviser)
.maxIterations(2)
.build();
SequentialAgent sequentialAgent =
SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("PostProcessing")
.description("Performs grammar and tone checks sequentially.")
.subAgents(grammarCheck, toneCheck)
.build();
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
storyGenerator, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "StoryGenerator",
Model: model,
Description: "Generates the initial story.",
Instruction: "You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat, based on the topic: {topic}",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create StoryGenerator agent: %v", err)
}
critic, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Critic",
Model: model,
Description: "Critiques the story.",
Instruction: "You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.",
OutputKey: "criticism",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Critic agent: %v", err)
}
reviser, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Reviser",
Model: model,
Description: "Revises the story based on criticism.",
Instruction: "You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Reviser agent: %v", err)
}
grammarCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "GrammarCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Checks grammar and suggests corrections.",
Instruction: "You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.",
OutputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create GrammarCheck agent: %v", err)
}
toneCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "ToneCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Analyzes the tone of the story.",
Instruction: "You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral' otherwise.",
OutputKey: "tone_check_result",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create ToneCheck agent: %v", err)
}
パート4:カスタムエージェントのインスタンス化と実行¶
最後に、StoryFlowAgentをインスタンス化し、通常通りRunnerを使用します。
# --- Create the custom agent instance ---
story_flow_agent = StoryFlowAgent(
name="StoryFlowAgent",
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
)
INITIAL_STATE = {"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house"}
# --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, state=INITIAL_STATE)
logger.info(f"Initial session state: {session.state}")
runner = Runner(
agent=story_flow_agent, # Pass the custom orchestrator agent
app_name=APP_NAME,
session_service=session_service
)
return session_service, runner
# --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async def call_agent_async(user_input_topic: str):
"""
Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
and runs the workflow.
"""
session_service, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
current_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
if not current_session:
logger.error("Session not found!")
return
current_session.state["topic"] = user_input_topic
logger.info(f"Updated session state topic to: {user_input_topic}")
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=f"Generate a story about: {user_input_topic}")])
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
final_response = "No final response captured."
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response() and event.content and event.content.parts:
logger.info(f"Potential final response from [{event.author}]: {event.content.parts[0].text}")
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
print("Agent Final Response: ", final_response)
final_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
print("Final Session State:")
import json
print(json.dumps(final_session.state, indent=2))
print("-------------------------------\n")
# --- Run the Agent ---
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard")
// Instantiate the custom agent, which encapsulates the workflow agents.
storyFlowAgent, err := NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create story flow agent: %v", err)
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
initialState := map[string]any{
"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house",
}
sessionInstance, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: appName,
UserID: userID,
State: initialState,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create session: %v", err)
}
userTopic := "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard"
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: storyFlowAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
input := genai.NewContentFromText("Generate a story about: "+userTopic, genai.RoleUser)
events := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionInstance.Session.ID(), input, agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeSSE,
})
var finalResponse string
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("An error occurred during agent execution: %v", err)
}
for _, part := range event.Content.Parts {
// Accumulate text from all parts of the final response.
finalResponse += part.Text
}
}
fmt.Println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
fmt.Println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse)
finalSession, err := sessionService.Get(ctx, &session.GetRequest{
UserID: userID,
AppName: appName,
SessionID: sessionInstance.Session.ID(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to retrieve final session: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("Final Session State:", finalSession.Session.State())
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
// Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
// and runs the workflow.
public static void runAgent(StoryFlowAgentExample agent, String userTopic) {
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(agent);
Map<String, Object> initialState = new HashMap<>();
initialState.put("topic", "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house");
Session session =
runner
.sessionService()
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialState), SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Initial session state: %s", session.state()));
session.state().put("topic", userTopic); // Update the state in the retrieved session
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Updated session state topic to: %s", userTopic));
Content userMessage = Content.fromParts(Part.fromText("Generate a story about: " + userTopic));
// Use the modified session object for the run
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
final String[] finalResponse = {"No final response captured."};
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse() && event.content().isPresent()) {
String author = event.author() != null ? event.author() : "UNKNOWN_AUTHOR";
Optional<String> textOpt =
event
.content()
.flatMap(Content::parts)
.filter(parts -> !parts.isEmpty())
.map(parts -> parts.get(0).text().orElse(""));
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("Potential final response from [%s]: %s", author, textOpt.orElse("N/A")));
textOpt.ifPresent(text -> finalResponse[0] = text);
}
});
System.out.println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
System.out.println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse[0]);
// Retrieve session again to see the final state after the run
Session finalSession =
runner
.sessionService()
.getSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, SESSION_ID, Optional.empty())
.blockingGet();
assert finalSession != null;
System.out.println("Final Session State:" + finalSession.state());
System.out.println("-------------------------------\n");
}
(注:インポートや実行ロジックを含む完全な実行可能コードは、以下のリンク先にあります。)
完全なコード例¶
Storyflowエージェント
# StoryFlowAgentの例の完全な実行可能コード
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import logging
from typing import AsyncGenerator
from typing_extensions import override
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent, BaseAgent, LoopAgent, SequentialAgent
from google.adk.agents.invocation_context import InvocationContext
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from google.adk.events import Event
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# --- Constants ---
APP_NAME = "story_app"
USER_ID = "12345"
SESSION_ID = "123344"
GEMINI_2_FLASH = "gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Configure Logging ---
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
# --- Custom Orchestrator Agent ---
class StoryFlowAgent(BaseAgent):
"""
Custom agent for a story generation and refinement workflow.
This agent orchestrates a sequence of LLM agents to generate a story,
critique it, revise it, check grammar and tone, and potentially
regenerate the story if the tone is negative.
"""
# --- Field Declarations for Pydantic ---
# Declare the agents passed during initialization as class attributes with type hints
story_generator: LlmAgent
critic: LlmAgent
reviser: LlmAgent
grammar_check: LlmAgent
tone_check: LlmAgent
loop_agent: LoopAgent
sequential_agent: SequentialAgent
# model_config allows setting Pydantic configurations if needed, e.g., arbitrary_types_allowed
model_config = {"arbitrary_types_allowed": True}
def __init__(
self,
name: str,
story_generator: LlmAgent,
critic: LlmAgent,
reviser: LlmAgent,
grammar_check: LlmAgent,
tone_check: LlmAgent,
):
"""
Initializes the StoryFlowAgent.
Args:
name: The name of the agent.
story_generator: An LlmAgent to generate the initial story.
critic: An LlmAgent to critique the story.
reviser: An LlmAgent to revise the story based on criticism.
grammar_check: An LlmAgent to check the grammar.
tone_check: An LlmAgent to analyze the tone.
"""
# Create internal agents *before* calling super().__init__
loop_agent = LoopAgent(
name="CriticReviserLoop", sub_agents=[critic, reviser], max_iterations=2
)
sequential_agent = SequentialAgent(
name="PostProcessing", sub_agents=[grammar_check, tone_check]
)
# Define the sub_agents list for the framework
sub_agents_list = [
story_generator,
loop_agent,
sequential_agent,
]
# Pydantic will validate and assign them based on the class annotations.
super().__init__(
name=name,
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
loop_agent=loop_agent,
sequential_agent=sequential_agent,
sub_agents=sub_agents_list, # Pass the sub_agents list directly
)
@override
async def _run_async_impl(
self, ctx: InvocationContext
) -> AsyncGenerator[Event, None]:
"""
Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
"""
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Starting story generation workflow.")
# 1. Initial Story Generation
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running StoryGenerator...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# Check if story was generated before proceeding
if "current_story" not in ctx.session.state or not ctx.session.state["current_story"]:
logger.error(f"[{self.name}] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return # Stop processing if initial story failed
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after generator: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 2. Critic-Reviser Loop
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running CriticReviserLoop...")
# Use the loop_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.loop_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from CriticReviserLoop: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Story state after loop: {ctx.session.state.get('current_story')}")
# 3. Sequential Post-Processing (Grammar and Tone Check)
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Running PostProcessing...")
# Use the sequential_agent instance attribute assigned during init
async for event in self.sequential_agent.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from PostProcessing: {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
# 4. Tone-Based Conditional Logic
tone_check_result = ctx.session.state.get("tone_check_result")
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone check result: {tone_check_result}")
if tone_check_result == "negative":
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
async for event in self.story_generator.run_async(ctx):
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Event from StoryGenerator (Regen): {event.model_dump_json(indent=2, exclude_none=True)}")
yield event
else:
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
pass
logger.info(f"[{self.name}] Workflow finished.")
# --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
story_generator = LlmAgent(
name="StoryGenerator",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words), on the following topic: {topic}""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Key for storing output in session state
)
critic = LlmAgent(
name="Critic",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story critic. Review the story provided: {{current_story}}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="criticism", # Key for storing criticism in session state
)
reviser = LlmAgent(
name="Reviser",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a story reviser. Revise the story provided: {{current_story}}, based on the criticism in
{{criticism}}. Output only the revised story.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="current_story", # Overwrites the original story
)
grammar_check = LlmAgent(
name="GrammarCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="grammar_suggestions",
)
tone_check = LlmAgent(
name="ToneCheck",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="""You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story provided: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.""",
input_schema=None,
output_key="tone_check_result", # This agent's output determines the conditional flow
)
# --- Create the custom agent instance ---
story_flow_agent = StoryFlowAgent(
name="StoryFlowAgent",
story_generator=story_generator,
critic=critic,
reviser=reviser,
grammar_check=grammar_check,
tone_check=tone_check,
)
INITIAL_STATE = {"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house"}
# --- Setup Runner and Session ---
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, state=INITIAL_STATE)
logger.info(f"Initial session state: {session.state}")
runner = Runner(
agent=story_flow_agent, # Pass the custom orchestrator agent
app_name=APP_NAME,
session_service=session_service
)
return session_service, runner
# --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
async def call_agent_async(user_input_topic: str):
"""
Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
and runs the workflow.
"""
session_service, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
current_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
if not current_session:
logger.error("Session not found!")
return
current_session.state["topic"] = user_input_topic
logger.info(f"Updated session state topic to: {user_input_topic}")
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=f"Generate a story about: {user_input_topic}")])
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
final_response = "No final response captured."
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response() and event.content and event.content.parts:
logger.info(f"Potential final response from [{event.author}]: {event.content.parts[0].text}")
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
print("Agent Final Response: ", final_response)
final_session = await session_service.get_session(app_name=APP_NAME,
user_id=USER_ID,
session_id=SESSION_ID)
print("Final Session State:")
import json
print(json.dumps(final_session.state, indent=2))
print("-------------------------------\n")
# --- Run the Agent ---
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard")
# StoryFlowAgentの例の完全な実行可能コード
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"iter"
"log"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/workflowagents/loopagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/workflowagents/sequentialagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// StoryFlowAgent is a custom agent that orchestrates a story generation workflow.
// It encapsulates the logic of running sub-agents in a specific sequence.
type StoryFlowAgent struct {
storyGenerator agent.Agent
revisionLoopAgent agent.Agent
postProcessorAgent agent.Agent
}
// NewStoryFlowAgent creates and configures the entire custom agent workflow.
// It takes individual LLM agents as input and internally creates the necessary
// workflow agents (loop, sequential), returning the final orchestrator agent.
func NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck agent.Agent,
) (agent.Agent, error) {
loopAgent, err := loopagent.New(loopagent.Config{
MaxIterations: 2,
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "CriticReviserLoop",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{critic, reviser},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create loop agent: %w", err)
}
sequentialAgent, err := sequentialagent.New(sequentialagent.Config{
AgentConfig: agent.Config{
Name: "PostProcessing",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{grammarCheck, toneCheck},
},
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to create sequential agent: %w", err)
}
// The StoryFlowAgent struct holds the agents needed for the Run method.
orchestrator := &StoryFlowAgent{
storyGenerator: storyGenerator,
revisionLoopAgent: loopAgent,
postProcessorAgent: sequentialAgent,
}
// agent.New creates the final agent, wiring up the Run method.
return agent.New(agent.Config{
Name: "StoryFlowAgent",
Description: "Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
SubAgents: []agent.Agent{storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent},
Run: orchestrator.Run,
})
}
// Run defines the custom execution logic for the StoryFlowAgent.
func (s *StoryFlowAgent) Run(ctx agent.InvocationContext) iter.Seq2[*session.Event, error] {
return func(yield func(*session.Event, error) bool) {
// Stage 1: Initial Story Generation
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story generator failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Check if story was generated before proceeding
currentStory, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("current_story")
if err != nil || currentStory == "" {
log.Println("Failed to generate initial story. Aborting workflow.")
return
}
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop
for event, err := range s.revisionLoopAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("loop agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 3: Post-Processing
for event, err := range s.postProcessorAgent.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("sequential agent failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration
toneResult, err := ctx.Session().State().Get("tone_check_result")
if err != nil {
log.Printf("Could not read tone_check_result from state: %v. Assuming tone is not negative.", err)
return
}
if tone, ok := toneResult.(string); ok && tone == "negative" {
log.Println("Tone is negative. Regenerating story...")
for event, err := range s.storyGenerator.Run(ctx) {
if err != nil {
yield(nil, fmt.Errorf("story regeneration failed: %w", err))
return
}
if !yield(event, nil) {
return
}
}
} else {
log.Println("Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.")
}
}
}
const (
modelName = "gemini-2.0-flash"
appName = "story_app"
userID = "user_12345"
)
func main() {
ctx := context.Background()
model, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
storyGenerator, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "StoryGenerator",
Model: model,
Description: "Generates the initial story.",
Instruction: "You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat, based on the topic: {topic}",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create StoryGenerator agent: %v", err)
}
critic, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Critic",
Model: model,
Description: "Critiques the story.",
Instruction: "You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.",
OutputKey: "criticism",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Critic agent: %v", err)
}
reviser, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "Reviser",
Model: model,
Description: "Revises the story based on criticism.",
Instruction: "You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.",
OutputKey: "current_story",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create Reviser agent: %v", err)
}
grammarCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "GrammarCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Checks grammar and suggests corrections.",
Instruction: "You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.",
OutputKey: "grammar_suggestions",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create GrammarCheck agent: %v", err)
}
toneCheck, err := llmagent.New(llmagent.Config{
Name: "ToneCheck",
Model: model,
Description: "Analyzes the tone of the story.",
Instruction: "You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral' otherwise.",
OutputKey: "tone_check_result",
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create ToneCheck agent: %v", err)
}
// Instantiate the custom agent, which encapsulates the workflow agents.
storyFlowAgent, err := NewStoryFlowAgent(
storyGenerator,
critic,
reviser,
grammarCheck,
toneCheck,
)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create story flow agent: %v", err)
}
// --- Run the Agent ---
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
initialState := map[string]any{
"topic": "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house",
}
sessionInstance, err := sessionService.Create(ctx, &session.CreateRequest{
AppName: appName,
UserID: userID,
State: initialState,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create session: %v", err)
}
userTopic := "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard"
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: storyFlowAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
input := genai.NewContentFromText("Generate a story about: "+userTopic, genai.RoleUser)
events := r.Run(ctx, userID, sessionInstance.Session.ID(), input, agent.RunConfig{
StreamingMode: agent.StreamingModeSSE,
})
var finalResponse string
for event, err := range events {
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("An error occurred during agent execution: %v", err)
}
for _, part := range event.Content.Parts {
// Accumulate text from all parts of the final response.
finalResponse += part.Text
}
}
fmt.Println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---")
fmt.Println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse)
finalSession, err := sessionService.Get(ctx, &session.GetRequest{
UserID: userID,
AppName: appName,
SessionID: sessionInstance.Session.ID(),
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to retrieve final session: %v", err)
}
fmt.Println("Final Session State:", finalSession.Session.State())
}
# StoryFlowAgentの例の完全な実行可能コード
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.BaseAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.InvocationContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.LoopAgent;
import com.google.adk.agents.SequentialAgent;
import com.google.adk.events.Event;
import com.google.adk.runner.InMemoryRunner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class StoryFlowAgentExample extends BaseAgent {
// --- Constants ---
private static final String APP_NAME = "story_app";
private static final String USER_ID = "user_12345";
private static final String SESSION_ID = "session_123344";
private static final String MODEL_NAME = "gemini-2.0-flash"; // Ensure this model is available
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(StoryFlowAgentExample.class.getName());
private final LlmAgent storyGenerator;
private final LoopAgent loopAgent;
private final SequentialAgent sequentialAgent;
public StoryFlowAgentExample(
String name, LlmAgent storyGenerator, LoopAgent loopAgent, SequentialAgent sequentialAgent) {
super(
name,
"Orchestrates story generation, critique, revision, and checks.",
List.of(storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent),
null,
null);
this.storyGenerator = storyGenerator;
this.loopAgent = loopAgent;
this.sequentialAgent = sequentialAgent;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- Define the individual LLM agents ---
LlmAgent storyGenerator =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("StoryGenerator")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Generates the initial story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story writer. Write a short story (around 100 words) about a cat,
based on the topic: {topic}
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Key for storing output in session state
.build();
LlmAgent critic =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Critic")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Critiques the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story critic. Review the story: {current_story}. Provide 1-2 sentences of constructive criticism
on how to improve it. Focus on plot or character.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("criticism") // Key for storing criticism in session state
.build();
LlmAgent reviser =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("Reviser")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Revises the story based on criticism.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a story reviser. Revise the story: {current_story}, based on the criticism: {criticism}. Output only the revised story.
""")
.inputSchema(null)
.outputKey("current_story") // Overwrites the original story
.build();
LlmAgent grammarCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("GrammarCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Checks grammar and suggests corrections.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a grammar checker. Check the grammar of the story: {current_story}. Output only the suggested
corrections as a list, or output 'Grammar is good!' if there are no errors.
""")
.outputKey("grammar_suggestions")
.build();
LlmAgent toneCheck =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ToneCheck")
.model(MODEL_NAME)
.description("Analyzes the tone of the story.")
.instruction(
"""
You are a tone analyzer. Analyze the tone of the story: {current_story}. Output only one word: 'positive' if
the tone is generally positive, 'negative' if the tone is generally negative, or 'neutral'
otherwise.
""")
.outputKey("tone_check_result") // This agent's output determines the conditional flow
.build();
LoopAgent loopAgent =
LoopAgent.builder()
.name("CriticReviserLoop")
.description("Iteratively critiques and revises the story.")
.subAgents(critic, reviser)
.maxIterations(2)
.build();
SequentialAgent sequentialAgent =
SequentialAgent.builder()
.name("PostProcessing")
.description("Performs grammar and tone checks sequentially.")
.subAgents(grammarCheck, toneCheck)
.build();
StoryFlowAgentExample storyFlowAgentExample =
new StoryFlowAgentExample(APP_NAME, storyGenerator, loopAgent, sequentialAgent);
// --- Run the Agent ---
runAgent(storyFlowAgentExample, "a lonely robot finding a friend in a junkyard");
}
// --- Function to Interact with the Agent ---
// Sends a new topic to the agent (overwriting the initial one if needed)
// and runs the workflow.
public static void runAgent(StoryFlowAgentExample agent, String userTopic) {
// --- Setup Runner and Session ---
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(agent);
Map<String, Object> initialState = new HashMap<>();
initialState.put("topic", "a brave kitten exploring a haunted house");
Session session =
runner
.sessionService()
.createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initialState), SESSION_ID)
.blockingGet();
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Initial session state: %s", session.state()));
session.state().put("topic", userTopic); // Update the state in the retrieved session
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("Updated session state topic to: %s", userTopic));
Content userMessage = Content.fromParts(Part.fromText("Generate a story about: " + userTopic));
// Use the modified session object for the run
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
final String[] finalResponse = {"No final response captured."};
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse() && event.content().isPresent()) {
String author = event.author() != null ? event.author() : "UNKNOWN_AUTHOR";
Optional<String> textOpt =
event
.content()
.flatMap(Content::parts)
.filter(parts -> !parts.isEmpty())
.map(parts -> parts.get(0).text().orElse(""));
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("Potential final response from [%s]: %s", author, textOpt.orElse("N/A")));
textOpt.ifPresent(text -> finalResponse[0] = text);
}
});
System.out.println("\n--- Agent Interaction Result ---");
System.out.println("Agent Final Response: " + finalResponse[0]);
// Retrieve session again to see the final state after the run
Session finalSession =
runner
.sessionService()
.getSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID, SESSION_ID, Optional.empty())
.blockingGet();
assert finalSession != null;
System.out.println("Final Session State:" + finalSession.state());
System.out.println("-------------------------------\n");
}
private boolean isStoryGenerated(InvocationContext ctx) {
Object currentStoryObj = ctx.session().state().get("current_story");
return currentStoryObj != null && !String.valueOf(currentStoryObj).isEmpty();
}
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runAsyncImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
// Implements the custom orchestration logic for the story workflow.
// Uses the instance attributes assigned by Pydantic (e.g., self.story_generator).
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Starting story generation workflow.", name()));
// Stage 1. Initial Story Generation
Flowable<Event> storyGenFlow = runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator");
// Stage 2: Critic-Reviser Loop (runs after story generation completes)
Flowable<Event> criticReviserFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
if (!isStoryGenerated(invocationContext)) {
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,() ->
String.format("[%s] Failed to generate initial story. Aborting after StoryGenerator.",
name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // Stop further processing if no story
}
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after generator: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(loopAgent, invocationContext, "CriticReviserLoop");
});
// Stage 3: Post-Processing (runs after critic-reviser loop completes)
Flowable<Event> postProcessingFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Story state after loop: %s",
name(), invocationContext.session().state().get("current_story")));
return runStage(sequentialAgent, invocationContext, "PostProcessing");
});
// Stage 4: Conditional Regeneration (runs after post-processing completes)
Flowable<Event> conditionalRegenFlow = Flowable.defer(() -> {
String toneCheckResult = (String) invocationContext.session().state().get("tone_check_result");
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Tone check result: %s", name(), toneCheckResult));
if ("negative".equalsIgnoreCase(toneCheckResult)) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is negative. Regenerating story...", name()));
return runStage(storyGenerator, invocationContext, "StoryGenerator (Regen)");
} else {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] Tone is not negative. Keeping current story.", name()));
return Flowable.empty(); // No regeneration needed
}
});
return Flowable.concatArray(storyGenFlow, criticReviserFlow, postProcessingFlow, conditionalRegenFlow)
.doOnComplete(() -> logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Workflow finished.", name())));
}
// Helper method for a single agent run stage with logging
private Flowable<Event> runStage(BaseAgent agentToRun, InvocationContext ctx, String stageName) {
logger.log(Level.INFO, () -> String.format("[%s] Running %s...", name(), stageName));
return agentToRun
.runAsync(ctx)
.doOnNext(event ->
logger.log(Level.INFO,() ->
String.format("[%s] Event from %s: %s", name(), stageName, event.toJson())))
.doOnError(err ->
logger.log(Level.SEVERE,
String.format("[%s] Error in %s", name(), stageName), err))
.doOnComplete(() ->
logger.log(Level.INFO, () ->
String.format("[%s] %s finished.", name(), stageName)));
}
@Override
protected Flowable<Event> runLiveImpl(InvocationContext invocationContext) {
return Flowable.error(new UnsupportedOperationException("runLive not implemented."));
}
}