コールバック:エージェントの振る舞いを監視、カスタマイズ、制御する¶
コールバックはADKの中核となる機能であり、エージェントの実行プロセスにフックするための強力なメカニズムを提供します。これにより、コアのADKフレームワークコードを変更することなく、事前に定義された特定のポイントでエージェントの振る舞いを監視、カスタマイズ、さらには制御することが可能になります。
コールバックとは? 本質的に、コールバックは開発者が定義する標準的な関数です。そして、エージェントを作成する際にこれらの関数をエージェントに関連付けます。ADKフレームワークは、主要なステージであなたの関数を自動的に呼び出し、監視や介入を可能にします。エージェントのプロセスにおけるチェックポイントのようなものだと考えてください。
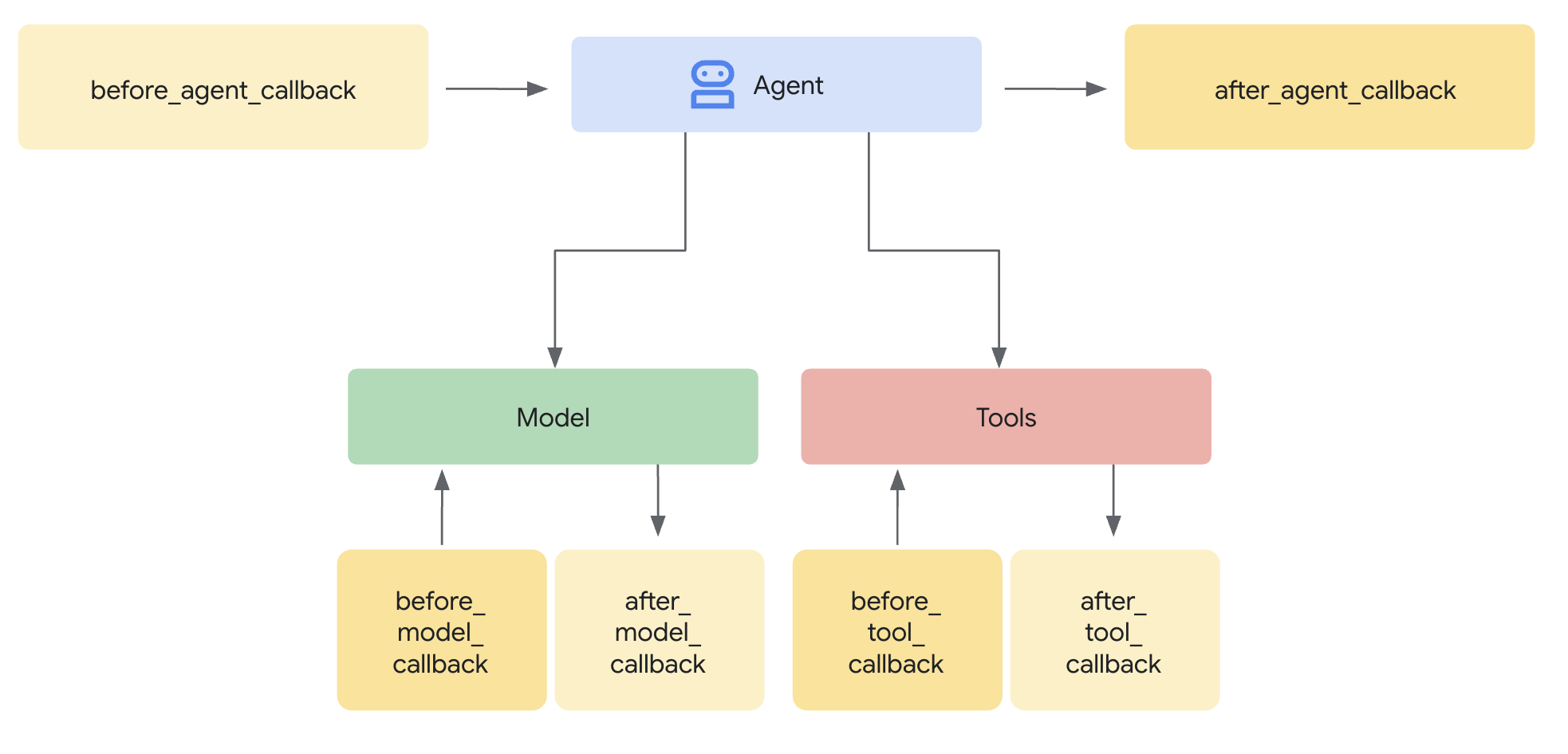
- エージェントがリクエストに対するメインの処理を開始する前と、完了した後: エージェントに何か(例:質問に答える)を依頼すると、エージェントは応答を導き出すために内部ロジックを実行します。
Before Agentコールバックは、その特定のリクエストに対するメインの処理が始まる直前に実行されます。After Agentコールバックは、エージェントがそのリクエストに対する全てのステップを終え、最終結果を準備した直後、しかし結果が返される直前に実行されます。- この「メインの処理」とは、その単一のリクエストを処理するためのエージェントの全体のプロセスを指します。これには、LLMを呼び出す決定、実際のLLM呼び出し、ツールを使用する決定、ツールの使用、結果の処理、そして最終的に回答を組み立てる過程が含まれる場合があります。これらのコールバックは、本質的に、入力を受け取ってからその一つの対話に対する最終的な出力を生成するまでの一連の流れ全体をラップします。
- 大規模言語モデル(LLM)にリクエストを送信する前、またはレスポンスを受信した後: これらのコールバック(
Before Model、After Model)により、LLMとの間でやり取りされるデータを具体的に検査または変更できます。 - ツール(Python関数や他のエージェントなど)を実行する前、または完了した後: 同様に、
Before Tool、After Toolコールバックは、エージェントによって呼び出されるツールの実行に特化した制御点を提供します。
なぜ使うのか? コールバックは大きな柔軟性を引き出し、高度なエージェント機能を可能にします。
- 監視とデバッグ: モニタリングやトラブルシューティングのために、重要なステップで詳細な情報をログに記録します。
- カスタマイズと制御: エージェントを流れるデータ(LLMリクエストやツールの結果など)を変更したり、独自のロジックに基づいて特定のステップを完全にバイパスしたりします。
- ガードレールの実装: 安全規則を強制し、入力/出力を検証したり、許可されていない操作を防いだりします。
- 状態管理: 実行中にエージェントのセッション状態を読み取ったり、動的に更新したりします。
- 統合と機能拡張: 外部のアクション(API呼び出し、通知)をトリガーしたり、キャッシングなどの機能を追加したりします。
Tip
セキュリティガードレールやポリシーを実装する際には、コールバックよりも モジュール性と柔軟性に優れたADKプラグインを使用してください。詳細は セキュリティガードレールのためのコールバックとプラグインを参照してください。
追加方法:
Code
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from typing import Optional
# --- Define your callback function ---
def my_before_model_logic(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
print(f"Callback running before model call for agent: {callback_context.agent_name}")
# ... your custom logic here ...
return None # Allow the model call to proceed
# --- Register it during Agent creation ---
my_agent = LlmAgent(
name="MyCallbackAgent",
model="gemini-2.0-flash", # Or your desired model
instruction="Be helpful.",
# Other agent parameters...
before_model_callback=my_before_model_logic # Pass the function here
)
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModel is a callback function that gets triggered before an LLM call.
func onBeforeModel(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModel Callback Triggered ---")
log.Printf("Model Request to be sent: %v\n", req)
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runBasicExample() {
const (
appName = "CallbackBasicApp"
userID = "test_user_123"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
// Register the callback function in the agent configuration.
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "SimpleAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModel},
}
simpleAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: simpleAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.Callbacks;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import java.util.Optional;
public class AgentWithBeforeModelCallback {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// --- Define your callback logic ---
Callbacks.BeforeModelCallbackSync myBeforeModelLogic =
(CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) -> {
System.out.println(
"Callback running before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// ... your custom logic here ...
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the model call to proceed,
// similar to returning None in the Python example.
// If you wanted to return a response and skip the model call,
// you would return Optional.of(yourLlmResponse).
return Optional.empty();
};
// --- Register it during Agent creation ---
LlmAgent myAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("MyCallbackAgent")
.model("gemini-2.0-flash") // Or your desired model
.instruction("Be helpful.")
// Other agent parameters...
.beforeModelCallbackSync(myBeforeModelLogic) // Pass the callback implementation here
.build();
}
}
コールバックのメカニズム:インターセプトと制御¶
ADKフレームワークがコールバックを実行できるポイント(例:LLMを呼び出す直前)に達すると、そのエージェントに対応するコールバック関数が提供されているかを確認します。もし提供されていれば、フレームワークはその関数を実行します。
コンテキストが鍵となります: コールバック関数は単独で呼び出されるわけではありません。フレームワークは特別なコンテキストオブジェクト(CallbackContext または ToolContext)を引数として提供します。これらのオブジェクトには、呼び出しの詳細、セッションの状態、アーティファクトやメモリなどのサービスへの参照を含む、エージェントの実行の現在状態に関する重要な情報が含まれています。これらのコンテキストオブジェクトを使用して、状況を理解し、フレームワークと対話します。(詳細は専用の「コンテキストオブジェクト」セクションを参照してください)。
フローの制御(コアメカニズム): コールバックの最も強力な側面は、その戻り値がエージェントのその後のアクションにどのように影響を与えるかにあります。これにより、実行フローをインターセプトし、制御します。
-
return None(デフォルトの動作を許可):- 具体的な戻り値の型は言語によって異なる場合があります。Javaでは、
Optional.empty()が同等の戻り値となります。言語固有のガイダンスについてはAPIドキュメントを参照してください。 - これは、コールバックが自身の処理(例:ロギング、検査、
llm_requestのような変更可能な入力引数の軽微な修正)を完了し、ADKエージェントが通常の操作を続行すべきであることを示す標準的な方法です。 before_*コールバック(before_agent,before_model,before_tool)の場合、Noneを返すと、シーケンスの次のステップ(エージェントロジックの実行、LLMの呼び出し、ツールの実行)が行われます。after_*コールバック(after_agent,after_model,after_tool)の場合、Noneを返すと、直前のステップで生成された結果(エージェントの出力、LLMのレスポンス、ツールの結果)がそのまま使用されます。
- 具体的な戻り値の型は言語によって異なる場合があります。Javaでは、
-
return <特定のオブジェクト>(デフォルトの動作を上書き):Noneの代わりに特定の型のオブジェクトを返すことで、ADKエージェントのデフォルトの動作を上書き(override)します。フレームワークはあなたが返したオブジェクトを使用し、通常なら続くはずのステップをスキップするか、生成されたばかりの結果を置き換えます。before_agent_callback→types.Content: エージェントのメイン実行ロジック (_run_async_impl/_run_live_impl) をスキップします。返されたContentオブジェクトは、直ちにそのターンにおけるエージェントの最終出力として扱われます。単純なリクエストを直接処理したり、アクセス制御を強制したりするのに便利です。before_model_callback→LlmResponse: 外部の大規模言語モデルへの呼び出しをスキップします。返されたLlmResponseオブジェクトは、LLMからの実際のレスポンスであるかのように処理されます。入力ガードレールの実装、プロンプトの検証、キャッシュされたレスポンスの提供に最適です。before_tool_callback→dictまたはMap: 実際のツール関数(またはサブエージェント)の実行をスキップします。返されたdictはツール呼び出しの結果として使用され、通常はLLMに返されます。ツールの引数検証、ポリシー制限の適用、モック/キャッシュされたツール結果を返すのに最適です。after_agent_callback→types.Content: エージェントの実行ロジックが生成したContentを置き換えます。after_model_callback→LlmResponse: LLMから受け取ったLlmResponseを置き換えます。出力のサニタイズ、標準的な免責事項の追加、LLMのレスポンス構造の変更に便利です。after_tool_callback→dictまたはMap: ツールが返したdictの結果を置き換えます。ツール出力をLLMに送り返す前に後処理したり標準化したりできます。
概念的なコード例(ガードレール):
この例は before_model_callback を使用したガードレールの一般的なパターンを示しています。
Code
# Copyright 2025 Google LLC
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
from google.adk.agents.callback_context import CallbackContext
from google.adk.models import LlmResponse, LlmRequest
from google.adk.runners import Runner
from typing import Optional
from google.genai import types
from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
GEMINI_2_FLASH="gemini-2.0-flash"
# --- Define the Callback Function ---
def simple_before_model_modifier(
callback_context: CallbackContext, llm_request: LlmRequest
) -> Optional[LlmResponse]:
"""Inspects/modifies the LLM request or skips the call."""
agent_name = callback_context.agent_name
print(f"[Callback] Before model call for agent: {agent_name}")
# Inspect the last user message in the request contents
last_user_message = ""
if llm_request.contents and llm_request.contents[-1].role == 'user':
if llm_request.contents[-1].parts:
last_user_message = llm_request.contents[-1].parts[0].text
print(f"[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '{last_user_message}'")
# --- Modification Example ---
# Add a prefix to the system instruction
original_instruction = llm_request.config.system_instruction or types.Content(role="system", parts=[])
prefix = "[Modified by Callback] "
# Ensure system_instruction is Content and parts list exists
if not isinstance(original_instruction, types.Content):
# Handle case where it might be a string (though config expects Content)
original_instruction = types.Content(role="system", parts=[types.Part(text=str(original_instruction))])
if not original_instruction.parts:
original_instruction.parts.append(types.Part(text="")) # Add an empty part if none exist
# Modify the text of the first part
modified_text = prefix + (original_instruction.parts[0].text or "")
original_instruction.parts[0].text = modified_text
llm_request.config.system_instruction = original_instruction
print(f"[Callback] Modified system instruction to: '{modified_text}'")
# --- Skip Example ---
# Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if "BLOCK" in last_user_message.upper():
print("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.")
# Return an LlmResponse to skip the actual LLM call
return LlmResponse(
content=types.Content(
role="model",
parts=[types.Part(text="LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")],
)
)
else:
print("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.")
# Return None to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return None
# Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback
my_llm_agent = LlmAgent(
name="ModelCallbackAgent",
model=GEMINI_2_FLASH,
instruction="You are a helpful assistant.", # Base instruction
description="An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback",
before_model_callback=simple_before_model_modifier # Assign the function here
)
APP_NAME = "guardrail_app"
USER_ID = "user_1"
SESSION_ID = "session_001"
# Session and Runner
async def setup_session_and_runner():
session_service = InMemorySessionService()
session = await session_service.create_session(app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID)
runner = Runner(agent=my_llm_agent, app_name=APP_NAME, session_service=session_service)
return session, runner
# Agent Interaction
async def call_agent_async(query):
content = types.Content(role='user', parts=[types.Part(text=query)])
session, runner = await setup_session_and_runner()
events = runner.run_async(user_id=USER_ID, session_id=SESSION_ID, new_message=content)
async for event in events:
if event.is_final_response():
final_response = event.content.parts[0].text
print("Agent Response: ", final_response)
# Note: In Colab, you can directly use 'await' at the top level.
# If running this code as a standalone Python script, you'll need to use asyncio.run() or manage the event loop.
await call_agent_async("write a joke on BLOCK")
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"strings"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent"
"google.golang.org/adk/agent/llmagent"
"google.golang.org/adk/model"
"google.golang.org/adk/model/gemini"
"google.golang.org/adk/runner"
"google.golang.org/adk/session"
"google.golang.org/genai"
)
// onBeforeModelGuardrail is a callback that inspects the LLM request.
// If it contains a forbidden topic, it blocks the request and returns a
// predefined response. Otherwise, it allows the request to proceed.
func onBeforeModelGuardrail(ctx agent.CallbackContext, req *model.LLMRequest) (*model.LLMResponse, error) {
log.Println("--- onBeforeModelGuardrail Callback Triggered ---")
// Inspect the request content for forbidden topics.
for _, content := range req.Contents {
for _, part := range content.Parts {
if strings.Contains(part.Text, "finance") {
log.Println("Forbidden topic 'finance' detected. Blocking LLM call.")
// By returning a non-nil response, we override the default behavior
// and prevent the actual LLM call.
return &model.LLMResponse{
Content: &genai.Content{
Parts: []*genai.Part{{Text: "I'm sorry, but I cannot discuss financial topics."}},
Role: "model",
},
}, nil
}
}
}
log.Println("No forbidden topics found. Allowing LLM call to proceed.")
// Returning nil allows the default LLM call to proceed.
return nil, nil
}
func runGuardrailExample() {
const (
appName = "GuardrailApp"
userID = "test_user_456"
)
ctx := context.Background()
geminiModel, err := gemini.NewModel(ctx, modelName, &genai.ClientConfig{})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create model: %v", err)
}
agentCfg := llmagent.Config{
Name: "ChatAgent",
Model: geminiModel,
BeforeModelCallbacks: []llmagent.BeforeModelCallback{onBeforeModelGuardrail},
}
chatAgent, err := llmagent.New(agentCfg)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create agent: %v", err)
}
sessionService := session.InMemoryService()
r, err := runner.New(runner.Config{
AppName: appName,
Agent: chatAgent,
SessionService: sessionService,
})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("Failed to create runner: %v", err)
}
import com.google.adk.agents.CallbackContext;
import com.google.adk.agents.LlmAgent;
import com.google.adk.events.Event;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmRequest;
import com.google.adk.models.LlmResponse;
import com.google.adk.runner.InMemoryRunner;
import com.google.adk.sessions.Session;
import com.google.genai.types.Content;
import com.google.genai.types.GenerateContentConfig;
import com.google.genai.types.Part;
import io.reactivex.rxjava3.core.Flowable;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
public class BeforeModelGuardrailExample {
private static final String MODEL_ID = "gemini-2.0-flash";
private static final String APP_NAME = "guardrail_app";
private static final String USER_ID = "user_1";
public static void main(String[] args) {
BeforeModelGuardrailExample example = new BeforeModelGuardrailExample();
example.defineAgentAndRun("Tell me about quantum computing. This is a test.");
}
// --- Define your callback logic ---
// Looks for the word "BLOCK" in the user prompt and blocks the call to LLM if found.
// Otherwise the LLM call proceeds as usual.
public Optional<LlmResponse> simpleBeforeModelModifier(
CallbackContext callbackContext, LlmRequest llmRequest) {
System.out.println("[Callback] Before model call for agent: " + callbackContext.agentName());
// Inspect the last user message in the request contents
String lastUserMessageText = "";
List<Content> requestContents = llmRequest.contents();
if (requestContents != null && !requestContents.isEmpty()) {
Content lastContent = requestContents.get(requestContents.size() - 1);
if (lastContent.role().isPresent() && "user".equals(lastContent.role().get())) {
lastUserMessageText =
lastContent.parts().orElse(List.of()).stream()
.flatMap(part -> part.text().stream())
.collect(Collectors.joining(" ")); // Concatenate text from all parts
}
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Inspecting last user message: '" + lastUserMessageText + "'");
String prefix = "[Modified by Callback] ";
GenerateContentConfig currentConfig =
llmRequest.config().orElse(GenerateContentConfig.builder().build());
Optional<Content> optOriginalSystemInstruction = currentConfig.systemInstruction();
Content conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction;
if (optOriginalSystemInstruction.isPresent()) {
Content originalSystemInstruction = optOriginalSystemInstruction.get();
List<Part> originalParts =
new ArrayList<>(originalSystemInstruction.parts().orElse(List.of()));
String originalText = "";
if (!originalParts.isEmpty()) {
Part firstPart = originalParts.get(0);
if (firstPart.text().isPresent()) {
originalText = firstPart.text().get();
}
originalParts.set(0, Part.fromText(prefix + originalText));
} else {
originalParts.add(Part.fromText(prefix));
}
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
originalSystemInstruction.toBuilder().parts(originalParts).build();
} else {
conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction =
Content.builder()
.role("system")
.parts(List.of(Part.fromText(prefix)))
.build();
}
// This demonstrates building a new LlmRequest with the modified config.
llmRequest =
llmRequest.toBuilder()
.config(
currentConfig.toBuilder()
.systemInstruction(conceptualModifiedSystemInstruction)
.build())
.build();
System.out.println(
"[Callback] Conceptually modified system instruction is: '"
+ llmRequest.config().get().systemInstruction().get().parts().get().get(0).text().get());
// --- Skip Example ---
// Check if the last user message contains "BLOCK"
if (lastUserMessageText.toUpperCase().contains("BLOCK")) {
System.out.println("[Callback] 'BLOCK' keyword found. Skipping LLM call.");
LlmResponse skipResponse =
LlmResponse.builder()
.content(
Content.builder()
.role("model")
.parts(
List.of(
Part.builder()
.text("LLM call was blocked by before_model_callback.")
.build()))
.build())
.build();
return Optional.of(skipResponse);
}
System.out.println("[Callback] Proceeding with LLM call.");
// Return Optional.empty() to allow the (modified) request to go to the LLM
return Optional.empty();
}
public void defineAgentAndRun(String prompt) {
// --- Create LlmAgent and Assign Callback ---
LlmAgent myLlmAgent =
LlmAgent.builder()
.name("ModelCallbackAgent")
.model(MODEL_ID)
.instruction("You are a helpful assistant.") // Base instruction
.description("An LLM agent demonstrating before_model_callback")
.beforeModelCallbackSync(this::simpleBeforeModelModifier) // Assign the callback here
.build();
// Session and Runner
InMemoryRunner runner = new InMemoryRunner(myLlmAgent, APP_NAME);
// InMemoryRunner automatically creates a session service. Create a session using the service
Session session = runner.sessionService().createSession(APP_NAME, USER_ID).blockingGet();
Content userMessage =
Content.fromParts(Part.fromText(prompt));
// Run the agent
Flowable<Event> eventStream = runner.runAsync(USER_ID, session.id(), userMessage);
// Stream event response
eventStream.blockingForEach(
event -> {
if (event.finalResponse()) {
System.out.println(event.stringifyContent());
}
});
}
}
None を返す場合と特定のオブジェクトを返す場合の違いというこのメカニズムを理解することで、エージェントの実行パスを正確に制御でき、コールバックはADKで洗練された信頼性の高いエージェントを構築するための不可欠なツールとなります。